How To Create or Delete a MySQL Database or User
Databases offer a method for easily managing large amounts of information over the web. They are necessary to run many web-based applications, such as bulletin boards, content management systems, and online retail shops.
Note: Resellers can create accounts with usernames up to 16 characters long. Please note that MySQL Databases and Usernames will only include the first 8 characters. For example:
- cPanel username: lengthyusername
- MySQL Database: lengthyu_wrdp1
- MySQL Username: lengthyu_johndoe
This article discusses the different features of the MySQL Database. Please click the links below for the instructions.
- Create or delete a MySQL database ↴
- Create or delete a database user ↴
- Define a user’s privileges and how important they are ↴
- Using the database ↴
This video will show you how effortless it is to create the database and the database user and assign that user to your new database. This is standard practice for anyone looking to install third-party programs that use MySQL databases manually.
Disclaimer: Your cPanel may look new, but the steps should be relatively the same.
Create or delete a MySQL database
How to create a MySQL database
- Log in to cPanel.
- Look for the Databases section, then click MySQL Databases. Take me there!
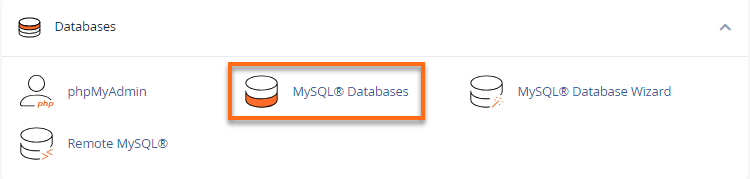
- In the New Database field, type a name for your database.
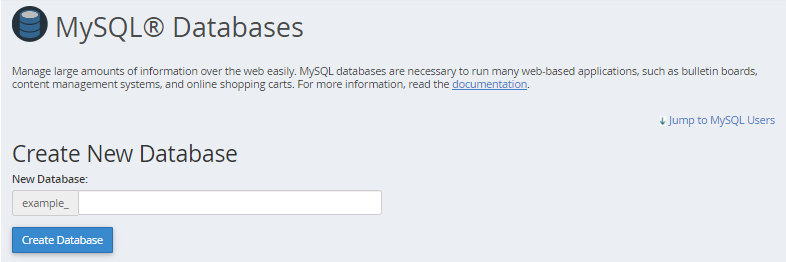
- Click Create Database.
- Click Go Back.
- The new database will appear in the Current Databases section.
How to delete a MySQL database
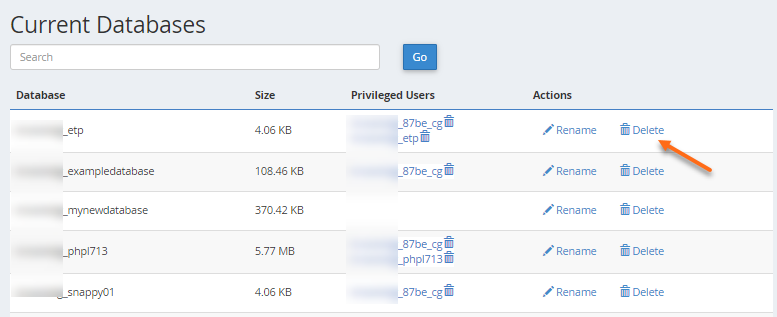
- Navigate to the Current Databases section of MySQL Databases.
- In the Actions column of the table, click Delete next to the database you wish to delete.
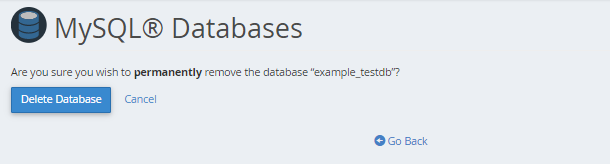
- Confirm that you wish to remove the database permanently.
Create or delete a database user
What is a MySQL user, and why is it important?
The MySQL user is a record in the MySQL server created for authentication purposes. This is different from your usernames when logging into Windows or even in your cPanel/WHM. Setting up a MySQL user provides more security to your website’s databases as you can assign permissions to each user. Aside from you, the website’s owner, you do not wish to grant just any user all access to your database.
After creating the database, you will need to create a user and assign privileges. Please note that MySQL user accounts must be created separately from mail and web administrator accounts.
How to create a database user
- Log in to cPanel.
- Look for the Databases section, then click MySQL Databases. Take me there!

- Click the Jump to MySQL Users link at the top-right corner of the page. You may also scroll a little bit down to the MySQL User section.
- Under Add New User, enter a username.
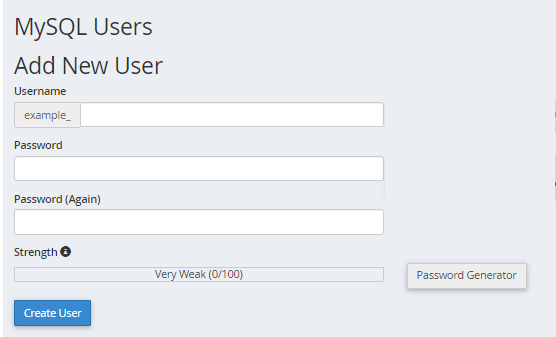
- Enter a password in the Password field.
- For help generating a strong password, click the Generate Password button.
- Once the password is confirmed, click on the Create User button.
How to delete a database user
- Navigate to the Current Users section of MySQL Databases.
- Locate the database user you wish to delete, then click its Delete icon.
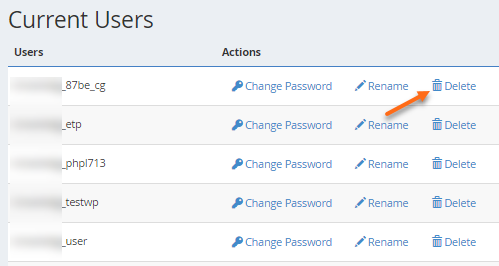
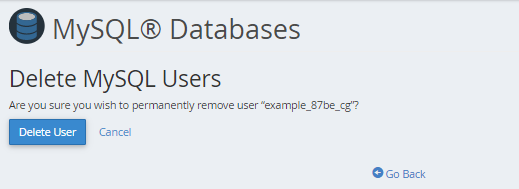
- Click the Delete User icon to confirm the deletion.
Define a user’s privileges and how important they are
You need specific users to have permission to perform website management tasks, like running queries or modifying databases. This is when we grant privileges. Privileges determine how a user can interact with the database. For example, privileges will dictate whether or not the user can add and delete information.
How to assign privileges to a database user
- Log in to cPanel.
- Look for the Databases section, then click MySQL Databases. Take me there!

- Under Add User to Database, select a user from the User dropdown menu.
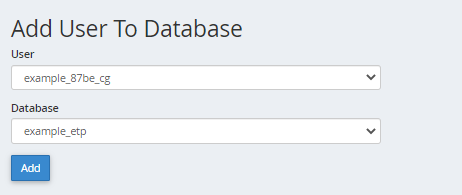
- From the Database dropdown menu, select the database you wish to allow the user access to.
- Click Add.
- Select the privileges you wish to grant the user or select ALL PRIVILEGES on the next page.
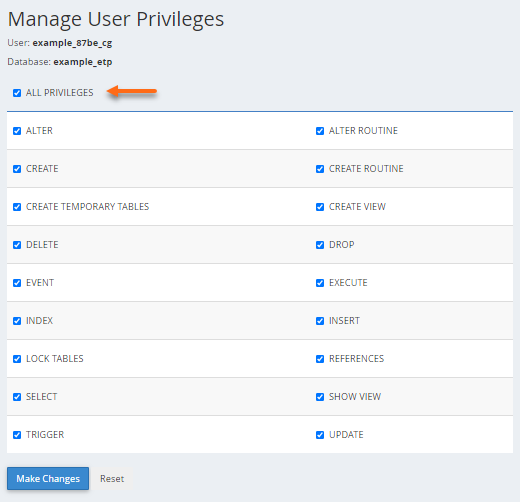
- Click Make Changes, then click Go Back.
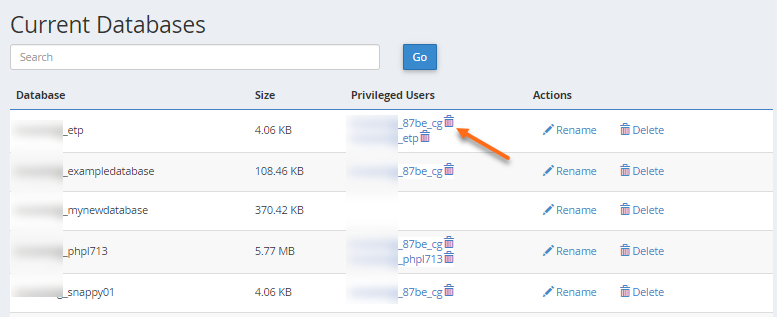
How to unassign a user from a database
- Navigate to the Current Databases section of MySQL Databases.
- Locate the database you wish to modify.
- In the Privileged Users column for that database, click the trash icon.
Using the database
Now that you can create databases and users and assign appropriate privileges, you can use the following articles as references in editing and connecting to your databases.
How to delete a database without using cPanel
The steps below are done using SSH. If you know how to use it, follow these steps; however, if you need help, contact us via phone or chat for assistance.
- Make a backup of the database with SSH using the command line below. Use your cPanel password.
username@domain [~] # mysqldump --password username_database > username_database.db Enter password: (cPanel Password) username@domain [~] # - Next, use the DROP DATABASE command inside of mysql to delete the database.
mysql> SHOW DATABASES LIKE "username_database"; +------------------------------+ | Database (username_database) | +------------------------------+ | username_database | +------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.02 sec) mysql> DROP DATABASE username_database; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> SHOW DATABASES LIKE "username_database"; Empty set (0.02 sec) mysql>
Go to the DROP DATABASE Statement link for further information on this command.
How to drop one or multiple users at a Time
Using the MySQL statement DROP USER allows you to remove user accounts and their privileges from the database.
Syntax:
DROP USER ‘user’@’host’;- User: The user account you want to drop.
- Host: The host server name of the user account. Format: ‘user_name’@’host_name’.
Example:
DROP USER ‘snappy01’@’localhost’;To DROP multiple user accounts, follow this format:
DROP USER ‘snappy01’@’localhost’, ‘snappy02’@’localhost’;How to grant Privileges in MySQL
To grant privileges to users in MySQL, you are first required to have the CREATE USER and GRANT privileges.
Syntax:
GRANT permission1, permission2 ON database_name TO 'user'@'localhost';Example:
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, DELETE ON example_db TO ‘snappy02’@’localhost’;
How to view privileges in MySQL
To show existing users and their privileges in MySQL, run the command SHOW GRANT.
Syntax:
SHOW GRANTS FOR 'database_user'@'localhost';Example:
SHOW GRANTS for ‘snappy02’@’localhost’;Sample Output:
mysql> SHOW GRANTS FOR ‘snappy02’@'localhost';
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Grants for snappy02@localhost |
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO `snappy02`@`localhost` |
| GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE ON `example_db`.* TO `snappy02`@`localhost` |
YOLO, right? yolo247casino is a bit of fun! They’ve got all the usual casino games, and the payouts seem fair. Just remember to gamble responsibly, mate!
Looking for a reliable 18plusgamblingcasinos site? This one looks promising. Always gamble responsibly, guys! Info here: 18plusgamblingcasinos
Wow, superb weblog format! How lengthy have you been blogging for? you make blogging look easy. The total look of your website is wonderful, as neatly as the content!
biggest escort directory Brazil
I’m really enjoying 66b1. Their website is great, and I found the games selection pretty good, and the bonuses are a nice little perk. Had a decent time overall! See what they offer: 66b1
Alright, signed up at jili77register. Registration was pretty quick and easy, not gonna lie. Fingers crossed for some good bonuses!
Want to see some good ‘gà chọi c1’ bouts? This site seems promising. Let’s get ready to rumble! gà chọi c1 .
11betcon – not a bad option to see some promotions and events. Check them here:11betcon!
Bot88bet… I’m curious about the ‘bot’ part. Do they have automated betting? Time to investigate! Hope it’s helpful, not just hype. Check it out here: bot88bet
Okay, so Nhatvipapk showed up on my phone, it has an APK. Haven’t used it a long time but let’s give it a try now. Check it out here: nhatvipapk